Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Akamatsu, Ken
no journal, ,
"How are the chemical structure, the yield, and the DNA damage spectrum caused by the ionizing radiations different by the radiations quality and their energy ?" The answer to this question becomes a vital information in clarifying the mutation and the carcinogenesis mechanism following to DNA damage. However, the unified view concerning this question has not been obtained because of a lot of uncertainties in the status of DNA, in the variety of DNA damage and in the distribution of radical scavengers and in the possibility of the directly and indirect effects, in the oxygen concentration, and furthermore in the artifact, etc., regardless of the long-term investigation for the past several ten years. Then, we have developed DNA damage spectrum analysis method that doesn't strictly stick to the chemical structure of individual damage and is not influenced easily by the weakness of irradiated DNA.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ouchi, Noriyuki
no journal, ,
Recent years, our understandings about the contribution of physical stimulation(cell adhesion or cell shape, etc.) to the DNA synthesis or apoptosisin the process of cell carcinogenesis have advanced, and the importance of the research to clarify these factors to the carcinogenesis is getting worth more and more. Here, we are going to introduce the mathematical model of tumor growth based on the morphological study.
Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sato, Takahiro; Yokota, Yuichiro; Wada, Seiichi*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Yokota, Wataru; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
We installed new focusing microbeam system at a vertical beam line of AVF cyclotron of TIARA, JAEA. New system is equipped with a quadruplet quadrupole lens system for higher spatial resolution and with an X, Y beam scanner for fast hitting of single ion to micron scaled samples like a biological cell. In vacuum, a microbeam generated by the system had spatial resolution of less than 1  m. The beam was extracted into the atmosphere, and its spatial distribution of ion was observed by irradiating ion track detector, CR39, at just beneath a vacuum window made by Kapton film of 8
m. The beam was extracted into the atmosphere, and its spatial distribution of ion was observed by irradiating ion track detector, CR39, at just beneath a vacuum window made by Kapton film of 8  m thick. The spatial resolution of beam extracted in air was less than 5
m thick. The spatial resolution of beam extracted in air was less than 5  m, indicating that finer microbeam was generated by new focusing microbeam system. New cell targeting system for this microbeam system, which is designed to target and irradiate biological materials more precisely, is currently under development.
m, indicating that finer microbeam was generated by new focusing microbeam system. New cell targeting system for this microbeam system, which is designed to target and irradiate biological materials more precisely, is currently under development.
Yokota, Yuichiro; Hase, Yoshihiro; Inoue, Masayoshi; Narumi, Issei; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
To consider LET effects is necessary for making clear the influence of environmental radiation to organisms, because high-LET radiation such as  -rays are included. In this study, we thus analyzed cell killing effect and DNA double-strand break (DSB) induction in tobacco cultured cells irradiated with high-LET heavy ions. As a result, cell killing effect and DSB induction per irradiated dose reached to maximum by the irradiation of carbon ions with LETs of 247 and 124-241 keV/
-rays are included. In this study, we thus analyzed cell killing effect and DNA double-strand break (DSB) induction in tobacco cultured cells irradiated with high-LET heavy ions. As a result, cell killing effect and DSB induction per irradiated dose reached to maximum by the irradiation of carbon ions with LETs of 247 and 124-241 keV/ m respectively. These findings were different from the LET dependencies that have been reported in mammalian cells and yeasts, suggesting that only data accumulated using mammals and yeasts are insufficient to decide the radiation impacts to all organisms.
m respectively. These findings were different from the LET dependencies that have been reported in mammalian cells and yeasts, suggesting that only data accumulated using mammals and yeasts are insufficient to decide the radiation impacts to all organisms.
 using heavy-ion microbeam
using heavy-ion microbeamSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ikeda, Daisuke*; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanase, Sumino*; Higashitani, Atsushi*; Ishii, Naoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Using  as a model multicellular organism, we push forward a heavy-ion microbeam irradiation individual-study. As for about 1.2 mm in a range of carbon ions in water, all cells and tissues of
as a model multicellular organism, we push forward a heavy-ion microbeam irradiation individual-study. As for about 1.2 mm in a range of carbon ions in water, all cells and tissues of  are microbeam irradiation objects. Sugimoto et al. showed DNA-damage-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in locally irradiated areas of
are microbeam irradiation objects. Sugimoto et al. showed DNA-damage-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in locally irradiated areas of  . We focus the nervous system of
. We focus the nervous system of  and study the effects of localized irradiation on salt chemotaxis learning behavior. However, the anesthetic method for fixation of animals is not usable because the whole body irradiation of
and study the effects of localized irradiation on salt chemotaxis learning behavior. However, the anesthetic method for fixation of animals is not usable because the whole body irradiation of  Co
Co  rays affected only transition stage of the conditioning for salt chemotaxis learning. Thus, now we are constructing the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation system for living target
rays affected only transition stage of the conditioning for salt chemotaxis learning. Thus, now we are constructing the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation system for living target  .
.
Watanabe, Ritsuko; Sato, Osamu*; Kubota, Asako*; Funabiki, Jun*; Saito, Kimiaki
no journal, ,
The purpose of this study is to estimate the yields and the configuration of DNA damages as well as the spatial distribution of the damages along to the tracks of heavy ions using the Monte Carlo simulation. A new Monte Carlo track structure code for any kind of ions from hydrogen to uranium has been developed and applied for simulation of the induction process of DNA damage. Induction of strand breaks and base damages were simulated with direct and the radical generation and diffusion using Monte Carlo methods for atomistic model of DNA. In our presentation, the framework of the developed track code for ions, OH radical yields, and the calculated DNA damage spectrum for selected types of ions for different energies will be shown and discussed by comparison with available experimental data.
Noguchi, Miho; Urushibara, Ayumi*; Yokoya, Akinari; Shikazono, Naoya
no journal, ,
Clustered DNA damage is defined as two or more lesions induced within 1-2 helical turns (10-20bp) of DNA. Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, especially DNA double strand breaks (DSB) are considered to be a major factor for radiation induced chromosomal aberration and cell death. Many studies have shown the experimental evidence of DSB induction and its repair efficiency, as well as intracellular signal transduction caused by DSB. It is predicted that the non-DSB clustered damage shows high biological effects. It is, however, technically difficult to directly detect non-DSB clustered damage site as well as its effect in living cells. In this study, we investigated the potential of single strand break (SSB) to influence the mutagenicity of 8-oxoG in Escherichia coli. The mutation frequency of 8-oxoG was enhanced by the SSB situated on opposite strand. When SSB was present in tandem on the same strand of an 8-oxoG, however, these clustered damages showed lower mutation frequency than a single 8-oxoG lesion. These results suggest that SSB opposed to 8-oxoG have an inhibitory effect on repair of 8-oxoG, but that, in the case of 8-oxoG and SSB positioned in tandem, 8-oxoG can be removed, at least partly, by the repair process of SSB. We propose that the mutagenic potential of 8-oxoG depends on whether SSB is located on either strand, same or opposite, to 8-oxoG.
Yokoya, Akinari; Urushibara, Ayumi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Shikazono, Naoya
no journal, ,
One of the goals of our study is to clarify the nature of clustered damage induced by densely ionizing radiation. We have developed a novel technique using DNA denaturation by which irradiated DNA is analyzed as single strand DNA. The prompt or enzymatically revealed additional single strand breaks which arise in both strands of pUC18 plasmid DNA, but do not induce a double strand break are measured as degradation of single strand DNA using gel electrophoresis. To avoid induction of heat labile strand breaks by high temperature generally used for a denaturation treatment, we have determined much lower denaturation temperature (37 degrees centigrade) using formamide (50% v/v). Obtained preliminary results will be presented.
Hata, Kuniki; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Nakagawa, Keiichi*; Nakagawa, Hidehiko*
no journal, ,
Edaravone, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one, is a newly developed free radical scavenger that has been approved in Japan as a neuroprotective drug since 2001. In the present work, the transient intermediates and the reactivity of edaravone towards  OH, N
OH, N
 , Br
, Br
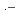 , SO
, SO
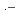 , and CCl
, and CCl O
O
 are investigated by pulse radiolysis techniques. The oxidation of edaravone by N
are investigated by pulse radiolysis techniques. The oxidation of edaravone by N
 , Br
, Br
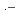 , SO
, SO
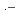 , and CCl
, and CCl O
O
 results in an absorption band with
results in an absorption band with 
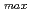 = 345 nm (
= 345 nm (
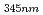 = 2600 M
= 2600 M cm
cm ), which is assigned to the edaravone radical formed by H-abstraction or electron transfer. However, the transient species produced by the reaction of edaravone with
), which is assigned to the edaravone radical formed by H-abstraction or electron transfer. However, the transient species produced by the reaction of edaravone with  OH radical shows an absorption band with
OH radical shows an absorption band with 
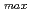 = 320 nm (
= 320 nm (
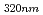 = 4900 M
= 4900 M cm
cm ). Accordingly, the main transient species by the reaction of edaravone with
). Accordingly, the main transient species by the reaction of edaravone with  OH radical in the absence of O
OH radical in the absence of O is attributed to OH-adducts. The rate constants of edaravone reacting with
is attributed to OH-adducts. The rate constants of edaravone reacting with  OH, N
OH, N
 , SO
, SO
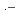 , and CCl
, and CCl O
O
 are estimated to be 8.5
are estimated to be 8.5 10
10 , 5.4
, 5.4 10
10 , 6.0
, 6.0 10
10 , and 5.1
, and 5.1 10
10 M
M s
s , respectively.
, respectively.
Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*
no journal, ,
The repair activities and mechanisms of both silybin and the analogues towards the oxidizing deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) hydroxyl radical adduct were investigated with pulse radiolytic technique. On pulse irradiation of nitrous oxide saturated 2.0 mM dGMP aqueous solution containing 0.1 mM silybin at neutral pH (2 mM phosphate buffer), the transient absorption spectrum of the dGMP hydroxyl radical adduct decays with the formation of phenoxyl radical of silybin within tens of microseconds. It indicates that there is a repair reaction between dGMP hydroxyl radical adduct and silybin. The rate constant of the repair reactions was calculated to be 1.0 10
10 L mol
L mol s
s for silybin. The repair activity of hesperetin, naringin and naringenin towards hydroxyl radical adducts of dGMP were also observed. Comparison of the rate constants of the four flavanones, silybin shows more effective reparation activities towards dGMP-OH adduct. The results indicate that dGMP radical can be rapidly repaired by silybin and analogues, which also demonstrated that non-enzymatic, fast repair is a universal repair mechanism of phenolic antioxidants.
for silybin. The repair activity of hesperetin, naringin and naringenin towards hydroxyl radical adducts of dGMP were also observed. Comparison of the rate constants of the four flavanones, silybin shows more effective reparation activities towards dGMP-OH adduct. The results indicate that dGMP radical can be rapidly repaired by silybin and analogues, which also demonstrated that non-enzymatic, fast repair is a universal repair mechanism of phenolic antioxidants.
Kusakabe, Takahiko*; Nakazato, Kyomi*; Takada, Hisashi*; Hisanaga, Etsuko*; Moon, H. D.*; Nakajima, Katsuyuki*; Suzuki, Keiji*; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sato, Takahiro; Arakawa, Kazuo; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Shikazono, Naoya; Pearson, C.*; Thacker, J.*; O'Neill, P.*
no journal, ,
Clustered DNA damage induced by a single radiation track is a unique feature of ionizing radiation. Recent in vitro studies have shown that the repair of lesions within clusters may be retarded, but less is known about the processing and the mutagenic effects of such clustered damage in vivo. Using a plasmid-based assay in Escherichia coli, we have investigated the mutagenic potential of bistranded clustered damage sites which consist of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG) and dihydrothymine (DHT) at defined separations. We found a significantly higher mutation frequency for the clustered DHT + 8-oxoG lesions than that for either a single 8-oxoG or a single DHT in wild-type and in glycosylase-deficient strains of  . Similar results were obtained with the 8-oxoG + AP cluster. To gain further insights on the processing of the DHT + 8-oxoG cluster, several potential intermediates were assessed. It was found that AP + AP and Gap + AP clusters strongly retard replication. These results led us to suggest that the base remaining within the cluster after removal of one of the base damage will not be further converted to an AP site or to a single strand break
. Similar results were obtained with the 8-oxoG + AP cluster. To gain further insights on the processing of the DHT + 8-oxoG cluster, several potential intermediates were assessed. It was found that AP + AP and Gap + AP clusters strongly retard replication. These results led us to suggest that the base remaining within the cluster after removal of one of the base damage will not be further converted to an AP site or to a single strand break  .
.
 -ray irradiation on the basal slowing response in
-ray irradiation on the basal slowing response in 
Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Fukamoto, Kana; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura; Tsuji, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Ito, Nobuhiko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura; Suzuki, Michiyo; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Omura, Motoko*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sora, Sakura; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oue, Atsushi*; Shimizu, Nobuaki*; Tanaka, Atsushi*; Otsuki, Takahiro*; Shinagawa, Masahiko*; Mori, Takahisa*; Saha, M. N.*; Ariful, H. S.*; Islam, S.*; Nakamura, Takako*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hino, Mizuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Tajika, Yuki*; Morimura, Yoshihiro*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Yorifuji, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English